Set:
In Python, a set is an unordered collection of unique elements. Sets are used when the existence of an element in a collection is more important than the order or how many times it occurs. Sets are mutable, meaning you can modify them after they are created. However, the elements of a set must be immutable (hashable), which means that elements like lists and other sets cannot be elements of a set.
Syntax:
my_set = {element1, element2, element3, ...}
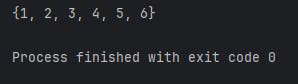
Example:
my_set = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 2, 4, 6}
print(my_set)
All the duplicate elements in the sets will not be printed because sets only saves the unique elements.
Output:
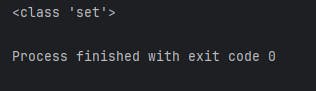
Check Data Type:
my_set = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
print(type(my_set))
Output:
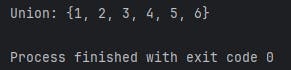
Sets Union:
set1 = {1, 2, 3}
set2 = {4, 5, 6}
union = set1.union(set2)
print("Union:", union)
Output:
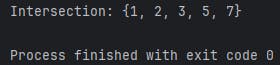
Sets Intersection:
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
set2 = {1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19}
intersection = set1.intersection(set2)
print("Intersection:", intersection)
Output: