Lecture # 19 - File Compression and Archiving
File Compression and Archiving in Linux
File Compression:
File compression is a process of reducing the size of a file. File compression is always performed using a lossless compression algorithm. This means no information is lost during the compression process. A compress archive can be fully restored to the original version when it is decompressed.
Compression:
gzip:
To compress a file using gzip, gzip [file-name] is used.
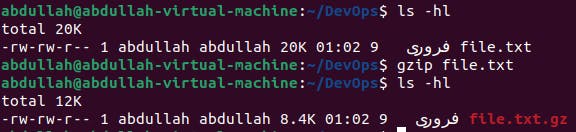
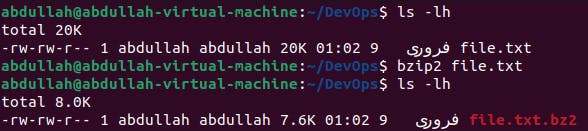
bzip2:
To compress a file using bzip2, bzip2 [file-name] is used.
Decopression:
gunzip:
To decompress a
gzipfile, gunzip is used. This command is written asgunzip [file-name].gz.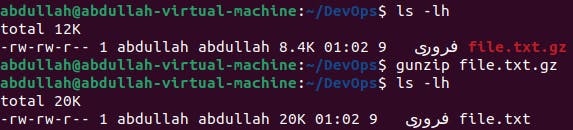
bunzip2:
To decompress a bzip2 file, bunzip2 is used. This command is written as
bunzip2 [file-name].bz2 .

File Archiving:
Archiving is the process of gathering up many files and bundling them together into a single large file. There are two ways to archive the files.
Archiving:
tar:
To create an archive using tar, tar -cf [archive-name.tar] [file/directory1] [file/directory2] is used.

zip:
To create an archive using zip, zip -r [archive-name.tar] [file/directory1] [file/directory2] is used.
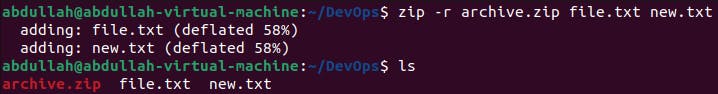
Unarchiving:
tar:
To unarchive using tar, tar -xf [name] is used.

zip:
To unarchive using zip,
unzip [name]is used.
