Lecture # 28 - Cron Job Scheduling
What is Cron? How is Cron Job Used? Cron Job Scheduling.
Cron:
Cron is a job scheduler in linux. It is used to run jobs periodically at fixed times, dates, or intervals. It performs specified operations at a predefined time or occurrence of an event without the intervention of the user. Cron is used to automate repeated tasks. It starts automatically from /etc/init.d on entering the multi-user run levels. Cron is a daemon (A background process executing non-interactive jobs).
Cron Jobs:
Tasks scheduled in cron are called cron jobs. Users can determine what kind of tasks they want to automate and when it shold be executed.
Cron Files:
Cron file is a simple text file that contains commands to run periodically at a specific time. The default system cron table or crontab configuration file is /etc/crontab .
Use Cases for Cron Job Scheduling:
Automated Backups:
Regularly schedule backups of databases, files, or entire systems.
System Maintenance:
Periodically run maintenance tasks such as clearing temporary files, updating software packages, or optimizing databases.
Log Rotation:
Rotate log files at specified intervals to manage disk space efficiently.
Scheduled Reports:
Generate and distribute reports automatically at scheduled times.
Data Synchronization:
Synchronize data between different systems or databases at regular intervals.
Security Scans:
Run security scans or vulnerability assessments on systems periodically.
Monitoring and Alerts:
Schedule scripts to monitor system health and send alerts if certain conditions are met.
File or Data Transfer:
Automate file transfers between servers or systems on a regular basis.
Periodic Cleanup:
Clean up temporary files, old backups, or other unnecessary data at scheduled times.
Database Maintenance:
Schedule tasks to optimize, backup, or perform other maintenance on databases.
Cron Job Scheduling Limitations:
Can't be distributed to multiple computers in a network.
Won't be able to repeat a job every 59 seconds or less.
Won't run again until the next scheduled time.
Crontab Syntax:
Crontab syntax consist of five fields and a command.

Minute (value between 0-59)
Hour (value between 0-23)
Day of Month (value between 1-31)
The month of the year (value between 1-12 or Jan-Dec)
Day of the week (value between 0-6 or Sun-Sat)
Command

Operators of Crontab:
Asterisk (*):
This operator signifies all possible values in a field. e.g. write an
*in a minute field to make the cronjob run every minute.Comma (,):
This operator is used for listing multiple values. e.g. writing
1,5in the day-of-week field will schedule the job to run every Monday and Friday.Hyphen (-):
This operator is used to determine range of the values. e.g. Write
6-9in the month-of-the-year field to schedule the job from June to September.Separator (/):
This operator is used to divide a value. e.g. If we want to run a script every twelve hours, write
*/12in the hour field.
Cron Job Special Strings:
@hourly:This string will run once in an hour. This command is written as
@hourly [command]. Its equivalent command is0 * * * * [command].@dailyor@midnight:These strings will run the task everyday at midnight. This command is written as
@daily [command]or@midnight [command]. Its equivalent command is \0 0 * * * [command].@weekly:This string will run the task once a week at midnight on Sunday. This command is written as
@weekly [command]. Its equivalent command is0 0 * * 0 [command].@monthly:This string will run the task once on the first day of every month. This command is written as
@monthly [command]. Its equivalent command is0 0 1 * * [command].@yearly:This string will run the task once a year at midnight on January 1st. This command is written as
@yearly [command]. Its equivalent command is0 0 1 1 * [command].@reboot:This string will run the task once during the system startup. This command is written as
@reboot /path/to/script/script.sh.
Writing Cron Jobs:
Every Minute:
* * * * * [command]Every 15 Minutes:
*/15 * * * * [command]On the 30th Minute of Every Hour:
30 * * * * [command]At the beginning of every hour:
0 * * * * [command]Everyday at midnight:
0 0 * * * [command]At 2am everyday:
0 2 * * * [command]Every 1st of the month:
0 0 1 * * [command]Every 15th of the month:
0 0 15 * * [command]On December 1st Midnight:
0 0 1 12 * [command]Saturdays at midnight:
0 0 * * 6 [command]Every weekday at 4am:
0 4 * * 1-5 [command]At 4am on Tuesdays and Thursdays:
0 4 * * 2,4 [command]Every Other Day at 37 Minutes Past the Hour:
37 1-23/2 * * * [command]Every 20 Minutes - Multiple Commands:
*/20 * * * * [command1]; [command2]On Saturdays and Sundays at 12 PM:
0 12 * * 6,0 [command]Monday to Friday - Every Hour 9 AM to 5 PM:
0 9-17 * * 1-5 [command]
Using Crontab:
Edit Crontab File:
To edit the crontab file
crontab -eis used.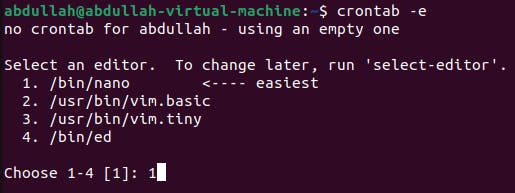
The file will be opened in the nano text editor.

List Existing Jobs:
To list the existing jobs
crontab -lis used.
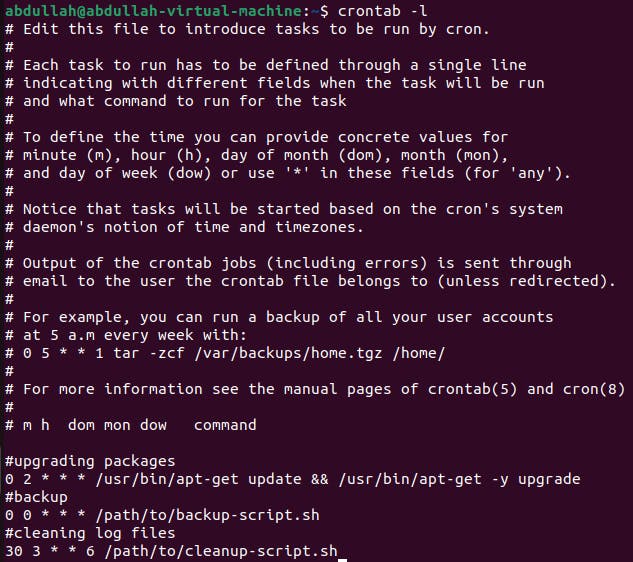
Delete All Jobs:
To delete all the jobs
crontab -ris used.
