Lecture # 4 - Virtual Machine, Virtualization & Virtualization Softwares
What is Virtual Machine? What is Virtualization? Where can we make Virtual Machines?
Virtual Machine (VM):
A virtual machine (VM) is a software-based emulation of a physical computer system. It allows you to run multiple operating systems (guest operating systems) simultaneously on a single physical machine (host system). Each virtual machine operates as an independent entity with its own virtual hardware components, including CPU, memory, storage, and network interfaces.
Virtualization:
Virtualization refers to the process of creating and running multiple virtual instances of computer hardware (such as CPU, memory, storage, and network interfaces) on a single physical machine. These virtual instances, known as virtual machines, operate as independent entities with their own operating systems and applications, but they share the underlying physical resources of the host machine.
Here's how virtualization works:
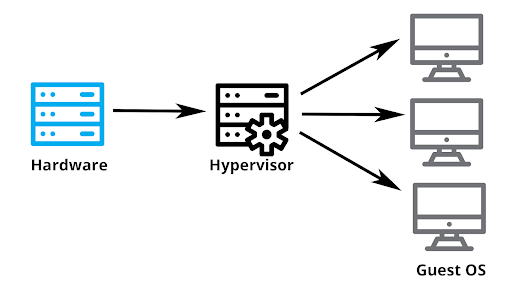
Hypervisor: A hypervisor (also known as a virtual machine monitor) is a software layer that creates and manages virtual machines on a physical host machine. The hypervisor abstracts and partitions the physical resources of the host machine, such as CPU, memory, and storage, into multiple virtualized instances that can run independently.
Virtual Hardware: Each virtual machine is provisioned with its own virtual hardware components, including virtual CPUs (vCPUs), virtual memory (RAM), virtual disks (storage), and virtual network interfaces. These virtual hardware components are emulated by the hypervisor and presented to the guest operating system running within the virtual machine.
Guest Operating System: Each virtual machine runs its own guest operating system, which interacts with the virtual hardware provided by the hypervisor. The guest operating system and its applications operate within the virtualized environment, unaware that they are running on virtualized hardware.
Isolation: Virtualization provides isolation between virtual machines, ensuring that each VM operates independently of other VMs on the same physical host. This isolation prevents conflicts and ensures security and reliability.
Virtualization Softwares:
VMware vSphere/ESXi:
VMware vSphere is a comprehensive virtualization platform for building and managing virtualized infrastructure. It includes VMware ESXi, a bare-metal hypervisor, along with management tools for provisioning, monitoring, and managing virtual machines. vSphere is widely used in enterprise environments for server virtualization, desktop virtualization (VDI), and cloud computing.

Microsoft Hyper-V:
Hyper-V is Microsoft's virtualization platform for creating and managing virtual machines on Windows Server environments. It provides features such as live migration, failover clustering, and integration with other Microsoft technologies like Active Directory and System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM).

Oracle VM VirtualBox:
VirtualBox is a free and open-source virtualization platform that runs on Windows, macOS, Linux, and Solaris hosts. It supports a wide range of guest operating systems and provides features such as snapshotting, shared folders, and virtual networking. VirtualBox is popular among developers, testers, and enthusiasts for creating and testing virtual environments on desktop computers.

